Matrices particulières
Matrice carrée
Une matrice est appelée carrée lorsque les nombres de lignes et de colonnes sont identiques.
Exemple:
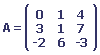
La matrice A possède trois lignes et trois colonnes, elle est donc carrée.
Vecteur ligne
Un vecteur ligne est une matrice qui possède une seule ligne.
Exemple:
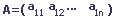
Vecteur colonne
Un vecteur colonne est une matrice qui possède une seule colonne.
Exemple:
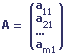
Matrice scalaire
Une matrice scalaire est une matrice qui ne possède qu'une seule ligne et une seule colonne (elle ne possède donc qu'un seul élément).
Exemple:
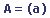
Matrice diagonale
Une matrice diagonale est une matrice carrée dont tous les éléments non compris dans la diagonale principale sont nuls.
Exemples:
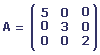 ou
ou 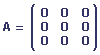
Matrice identité
Une matrice identité (ou unité) est une matrice diagonale dont les éléments de la diagonale principale sont de valeur 1.
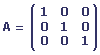
Matrice triangulaire
Une matrice triangulaire est une matrice carrée dont les éléments d'un même côté de la diagonale principale sont de valeur 0.
Matrice triangulaire supérieure
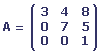
Matrice triangulaire inférieure
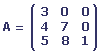
Transposée d'une matrice
Nous obtenons la transposée d'une matrice en permutant les lignes et les colonnes:
Remarques:
- La transposée de la matrice A se note donc tA.
- La transposée de la matrice de format m*n est une matrice de format n*m.
- Si tA=A, nous pouvons dire que la matrice est symétrique (elle doit donc être carrée).
- Si tA=-A, nous pouvons dire que la matrice est antisymétrique.
English translation
You have asked to visit this site in English. For now, only the interface is translated, but not all the content yet.If you want to help me in translations, your contribution is welcome. All you need to do is register on the site, and send me a message asking me to add you to the group of translators, which will give you the opportunity to translate the pages you want. A link at the bottom of each translated page indicates that you are the translator, and has a link to your profile.
Thank you in advance.
Document created the 19/03/2002, last modified the 07/04/2023
Source of the printed document:https://www.gaudry.be/en/matrices2.html
The infobrol is a personal site whose content is my sole responsibility. The text is available under CreativeCommons license (BY-NC-SA). More info on the terms of use and the author.


