11 Visual effects
Contents
11.1 Overflow and clipping
Generally, the content of a block box is confined to the content edges of the box. In certain cases, a box may overflow, meaning its content lies partly or entirely outside of the box, e.g.:
- A line cannot be broken, causing the line box to be wider than the block box.
- A block-level box is too wide for the containing block. This may happen when an element's 'width' property has a value that causes the generated block box to spill over sides of the containing block.
- An element's height exceeds an explicit height assigned to the containing block (i.e., the containing block's height is determined by the 'height' property, not by content height).
- A box is positioned absolutely.
- It has negative margins.
Whenever overflow occurs, the 'overflow' property specifies how (and whether) a box is clipped. The 'clip' property specifies the size and shape of the clipping region. Specifying a small clipping region may cause clipping of otherwise visible contents.
11.1.1 Overflow: the 'overflow' property
- 'overflow'
-
Value: visible | hidden | scroll | auto | inherit Initial: visible Applies to: block-level and replaced elements Inherited: no Percentages: N/A Media: visual
This property specifies whether the content of a block-level element is clipped when it overflows the element's box (which is acting as a containing block for the content). Values have the following meanings:
- visible
- This value indicates that content is not clipped, i.e., it may be rendered outside the block box.
- hidden
- This value indicates that the content is clipped and that no scrolling mechanism should be provided to view the content outside the clipping region; users will not have access to clipped content. The size and shape of the clipping region is specified by the 'clip' property.
- scroll
- This value indicates that the content is clipped and that if the user agent uses scrolling mechanism that is visible on the screen (such as a scroll bar or a panner), that mechanism should be displayed for a box whether or not any of its content is clipped. This avoids any problem with scrollbars appearing and disappearing in a dynamic environment. When this value is specified and the target medium is 'print' or 'projection', overflowing content should be printed.
- auto
- The behavior of the 'auto' value is user agent-dependent, but should cause a scrolling mechanism to be provided for overflowing boxes.
Even if 'overflow' is set to 'visible', content may be clipped to a UA's document window by the native operating environment.
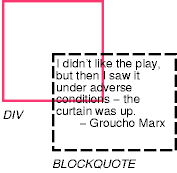
Consider the following example of a block quotation (BLOCKQUOTE) that is too big for its containing block (established by a DIV). Here is the source document:
<DIV> <BLOCKQUOTE> <P>I didn't like the play, but then I saw it under adverse conditions - the curtain was up. <DIV class="attributed-to">- Groucho Marx</DIV> </BLOCKQUOTE> </DIV>
Here is the style sheet controlling the sizes and style of the generated boxes:
DIV { width : 100px; height: 100px;
border: thin solid red;
}
BLOCKQUOTE { width : 125px; height : 100px;
margin-top: 50px; margin-left: 50px;
border: thin dashed black
}
DIV.attributed-to { text-align : right; }
The initial value of 'overflow' is 'visible', so the BLOCKQUOTE would be formatted without clipping, something like this:
Setting 'overflow' to 'hidden' for the DIV element, on the other hand, causes the BLOCKQUOTE to be clipped by the containing block:
A value of 'scroll' would tell UAs that support a visible scrolling mechanism to display one so that users could access the clipped content.
11.1.2 Clipping: the 'clip' property
A clipping region defines what portion of an element's rendered content is visible. By default, the clipping region has the same size and shape as the element's box(es). However, the clipping region may be modified by the 'clip' property.
The 'clip' property applies to elements that have a 'overflow' property with a value other than 'visible'. Values have the following meanings:
- auto
- The clipping region has the same size and location as the element's box(es).
- <shape>
- In CSS2, the only valid <shape> value is:
rect (<top> <right> <bottom> <left>)
where <top>, <bottom> <right>, and <left> specify offsets from the
respective sides of the box.
<top>, <right>, <bottom>, and <left> may either have a <length> value or 'auto'. Negative lengths are permitted. The value 'auto' means that a given edge of the clipping region will be the same as the edge of the element's generated box (i.e., 'auto' means the same as '0'.)
When coordinates are rounded to pixel coordinates, care should be taken that no pixels remain visible when <left> + <right> is equal to the element's width (or <top> + <bottom> equals the element's height), and conversely that no pixels remain hidden when these values are 0.
The element's ancestors may also have clipping regions (in case their 'overflow' property is not 'visible'); what is rendered is the intersection of the various clipping regions.
If the clipping region exceeds the bounds of the UA's document window, content may be clipped to that window by the native operating environment.
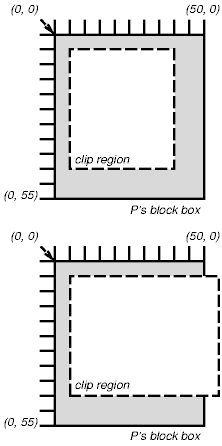
The following two rules:
P { clip: rect(5px, 10px, 10px, 5px); }
P { clip: rect(5px, -5px, 10px, 5px); }
will create the rectangular clipping regions delimited by the dashed lines in the following illustrations:
Note. In CSS2, all clipping regions are rectangular. We anticipate future extensions to permit non-rectangular clipping.
11.2 Visibility: the 'visibility' property
- 'visibility'
-
Value: visible | hidden | collapse | inherit Initial: inherit Applies to: all elements Inherited: no Percentages: N/A Media: visual
The 'visibility' property specifies whether the boxes generated by an element are rendered. Invisible boxes still affect layout (set the 'display' property to 'none' to suppress box generation altogether). Values have the following meanings:
- visible
- The generated box is visible.
- hidden
- The generated box is invisible (fully transparent), but still affects layout.
- collapse
- Please consult the section on dynamic row and column effects in tables. If used on elements other than rows or columns, 'collapse' has the same meaning as 'hidden'.
This property may be used in conjunction with scripts to create dynamic effects.
In the following example, pressing either form button invokes a user-defined script function that causes the corresponding box to become visible and the other to be hidden. Since these boxes have the same size and position, the effect is that one replaces the other. (The script code is in a hypothetical script language. It may or may not have any effect in a CSS-capable UA.)
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<STYLE type="text/css">
<!--
#container1 { position: absolute;
top: 2in; left: 2in; width: 2in }
#container2 { position: absolute;
top: 2in; left: 2in; width: 2in;
visibility: hidden; }
-->
</STYLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<P>Choose a suspect:</P>
<DIV id="container1">
<IMG alt="Al Capone"
width="100" height="100"
src="suspect1.jpg">
<P>Name: Al Capone</P>
<P>Residence: Chicago</P>
</DIV>
<DIV id="container2">
<IMG alt="Lucky Luciano"
width="100" height="100"
src="suspect2.jpg">
<P>Name: Lucky Luciano</P>
<P>Residence: New York</P>
</DIV>
<FORM method="post"
action="http://www.suspect.org/process-bums">
<P>
<INPUT name="Capone" type="button"
value="Capone"
onclick='show("container1");hide("container2")'>
<INPUT name="Luciano" type="button"
value="Luciano"
onclick='show("container2");hide("container1")'>
</FORM>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Document created the 04/02/2006, last modified the 26/10/2018
Source of the printed document:https://www.gaudry.be/en/css-rf-/visufx.html
The infobrol is a personal site whose content is my sole responsibility. The text is available under CreativeCommons license (BY-NC-SA). More info on the terms of use and the author.
References
These references and links indicate documents consulted during the writing of this page, or which may provide additional information, but the authors of these sources can not be held responsible for the content of this page.
The author This site is solely responsible for the way in which the various concepts, and the freedoms that are taken with the reference works, are presented here. Remember that you must cross multiple source information to reduce the risk of errors.